Google searches are key to search engine optimization (SEO), which is a crucial part of creating an eCommerce site that drives traffic. And keeping up with changes in search engines to improve your Google rankings is hard.
Especially when Google changes every day.
Also, the ten blue links from Google searches don’t drive as much organic traffic as they used to.

Why? Due to new SERP features.
These new SERP (SERP is short for “search engine results page”) features have improved the experience for users, but are also making the process more complicated for businesses.
And if you ask yourself: how to position my web page?, and you want to improve your search engine positioning (specifically, your positioning in Google), you must perfectly understand the rules of the game.
In this article, you will learn what SERPs are, what SEO and SEM are. Plus, you’ll learn the many Google SERP features in effect in 2021 and how to improve your search engine rankings.
So, let’s get started!
Google Advanced Search: What are Google SERPs?
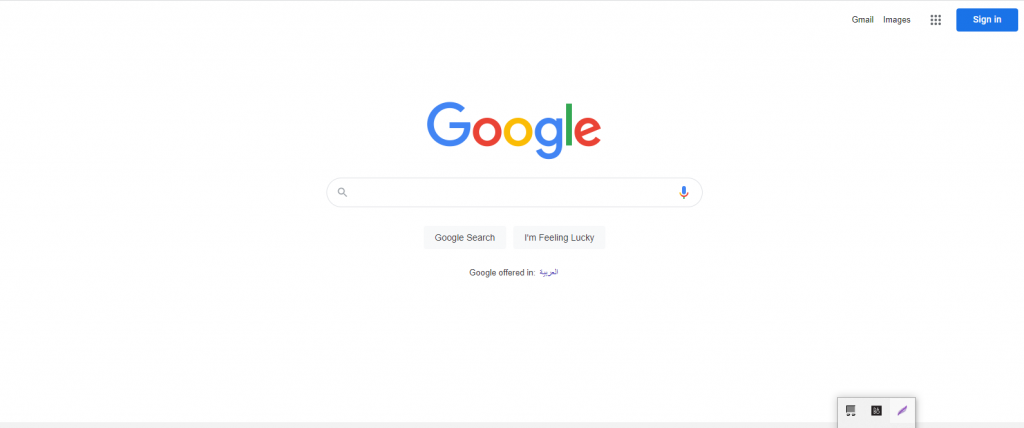
To learn how to improve your internet positioning, we first have to talk about the SERPs. SERP, or search engine results page, is the page that is displayed by search engines in response to user searches.
Let’s look at an example of a Google SERP:

The term SERP is not exclusive to a specific search engine: Google, Bing, and Yahoo show SERPs to users.
And to date, no two SERPs are the same. They are personalized for each user. That’s why you’ll sometimes see different search results when searching on different devices or from new locations.
SERP, why is it important?
When we talk about SERP, we refer to search engine optimization but we emphasize optimization to improve Google positioning.
Why? Because Google is king.
Seriously, when was the last time you used a search engine other than Google? People no longer even “ search for something”, “ Google it ”.
Also, take a look at the stats.
The following graph shows the search trend in the United States, according to different search engines:

As of April 2021, Google generated 62.7% of all top search queries in the United States, followed by Microsoft at 24.8% and Verizon Media (formerly Oath and Yahoo) at 11.6%.
And when it comes to mobile search in the US, Google again leads the market with a 93% share.
But that is not all.
Google’s dominance is even stronger in other big markets like the UK and Germany, where its market share ranges from 90 to 94 percent.
What is SERP in digital marketing?
SERP marketing is the process of promoting a business within the results of a search engine. There are two types of SERP marketing:
The most effective SERP marketing strategies use both SEO and SEM to achieve their business goals.
Let’s take a look at each one.
What is SEO?
The definition of SEO tells us that it is search engine optimization, and it is the process of having a high ranking in the SERPs organically (and increasing the positioning in Google). Organic means you don’t need to use payment methods (such as Google Ads ). So if you ask yourself: how to position my website on Google for free? The answer is through organic traffic.
There are many strategies and techniques in SEO. Two of the main ones are content marketing and backlinks (external links that point from other pages to your own).
With content marketing, the goal is to create content for a specific keyword, and that is meant to rank , giving you a higher position and maximum exposure in the SERPs. You can also try creating an external link profile with websites that have a high online presence. In other words, try searching Google for successful websites to link to your content, which will improve your online presence (and SERP ranking).
Let’s be honest: it takes time, dedication and experience to be successful in the SERP through organic SEO . However, the results are worth it.
Why?
The higher the SERP, the more clicks you will get .

On the first page of Google alone, the top five organic results account for more than 67% of clicks, while results 6-10 account for less than 4 percent.
Additionally, high-ranking organic content will generally maintain its position in the SERPs for an extended period of time and at no cost. So it is a more sustainable and long-lasting marketing channel.https://www.youtube.com/embed/Iydb1AjI7zs?feature=emb_title&v=Iydb1AjI7zs
What is SEM?
SEM stands for search engine marketing and is the process of acquiring search engine traffic through paid listings and advertisements. One of the most common SEM channels is Google Ads (formerly known as AdWords). These paid listings appear in Google above and below the organic search results, as well as in the sidebar.
Each paid listing is generated for specific keywords, and is usually charged for each click on each ad, hence the name Pay Per Click or PPC.
Google ad listings have a small “ad” badge to identify them as a paid listing, like in this example:

While paid ad results may not have the staying power of organic listings, they also have their benefits.
First of all, the return on investment (ROI) is faster.
With a well-targeted Google Ads campaign, you can go straight to the top of the SERPs and expose your business to targeted customers.
Also, while paid results may not return click-through rates (CTRs) as high as organic listings, Google PPC or pay-per-click ads return an average CTR of 2 percent , and if these are clicked on it ‘s very likely to convert.
But that is not all.
Paid results also bring a suite of analytics that provides a path to higher CTRs and conversions. And this knowledge is invaluable when optimizing your SEO efforts.
That is why the best SERP marketing combines SEO and SEM.
What are SERP features?
A SERP feature is any listing on a search engine results page that is not a standard organic result. These features are designed to provide better search results as the SERPs will show you more relevant and detailed information.
To understand the scope of SERP features, here’s what organic Google search results looked like a decade ago:

And for comparison, here’s a picture of a Google Advanced Search in 2021 with four different SERP features: Shopping, Ads, Top Stories, and Organic Results.

Clearly, a lot has changed since then.
Today, Google SERPs are much more useful, relevant, and accurate. Google is trying to shorten the amount of time and effort it takes for users to find what they’re looking for, and ecommerce businesses have to keep up.
How to Rank in Google: Organic Google SERP Features in 2021
Google constantly updates SERP features. This means that today, there are countless ways to get your business to the top of the SERPs and improve your search engine rankings.
Here’s a rundown of Google’s SERP features in 2021:
enriched responses
Rich responses are also known as answer boxes, quick responses, or direct responses. They are often shown in the SERPs when you ask simple questions like: “what time is it in the UK?”, or “what is a steam engine?”
Google does not credit rich answer sources because the information is said to be part of the public domain.
The image below shows an example of a rich response:
Rich results
A rich result (formerly known as a rich snippet) is similar to a regular Google SERP listing, except it contains more information than the standard title, meta description, and URL. Additional information shows customer ratings, prices, or additional links.
Website operators can add a structured data margin like Schema.org to optimize their content for Google’s rich results.
In the image below, you can see a rich result for Google Pixel 3 showing customer ratings and additional links:
Rich card (mobile devices)
Rich cards are the mobile-optimized version of rich results. Most Google searches are done on mobile devices, so it’s important to have a mobile strategy in place.
 knowledge cards
knowledge cards
Knowledge Cards work similarly to Rich Cards, except they are based on specific data. For example, if you search for “population in Bozeman”, you will see a knowledge card that shows you the following:
 And since these are based on specific data, it is difficult to rank for these results.
And since these are based on specific data, it is difficult to rank for these results.
knowledge graphs
Knowledge graphs are displayed above the organic results or in the right sidebar. They often include images, facts, maps, and related search topics. This SERP feature is often displayed for queries about certain topics, places, or people.
To create knowledge graphs, Google pulls information from its own Google Maps data, as well as from external sources like Wikipedia.
The following image shows us a knowledge graph derived from the search “London:”
knowledge panels
Knowledge panels are almost identical to knowledge graphs, unlike Google only pulls information from Google Maps or My Business. That is why the knowledge panels are displayed for queries about brands, businesses, or organizations.
Knowledge panels often include images, facts, social media links, and related searches.
The image below shows us a knowledge panel about Shopify :
Local 3-Pack
A local 3-pack is a SERP feature that contains a map and a list of three local businesses as a rich result. Local 3-packs are typically displayed for inquiries about nearby businesses or organizations.
Users searching for local businesses often have a commercial intent. Therefore, getting a position in a local 3-pack can do wonders for attracting new customers.
The image below shows a local 3-pack derived from a Google search for “best yoga studios in Berlin”:
 However, this SERP feature is only available to businesses with physical locations, so if you have an online dropshipping business, this is not an option for you.
However, this SERP feature is only available to businesses with physical locations, so if you have an online dropshipping business, this is not an option for you.
image groups
This SERP feature is displayed for any search that refers specifically to images or visual results. Almost 23% of Google SERPs show images, and this percentage is increasing.
Unfortunately for businesses, when a user clicks on an image, it links to Google Images and not to the website the image came from.
The following example shows a group of images derived from the query “cat chasing a mouse”:
 Also, image packs can be displayed in different ways. The following example shows a smaller image pack in response to the search for “cat in a tree”:
Also, image packs can be displayed in different ways. The following example shows a smaller image pack in response to the search for “cat in a tree”:
 This also works in your favor for Google image searches. According to Jumpshot and Moz, 27% of all searches were for images. And the difference here is that when a user clicks on an image, it links to your website.
This also works in your favor for Google image searches. According to Jumpshot and Moz, 27% of all searches were for images. And the difference here is that when a user clicks on an image, it links to your website.
Videos
Google also shows results for three YouTube videos, as in the example below. A search for “how to change a tire” brings up three quick video thumbnails, and users can scroll right to see more related videos.
site links
This SERP feature provides a broad pool of links from a specific domain. Sitelinks are typically displayed when a user searches for a specific website or organization. Google’s goal is to allow users to navigate directly to the page of the website they are looking for.
The image below shows the sitelinks for different pages on the Oberlo website.
vertical search
Vertical search appears at the top of the page when Google needs to display information from different categories, such as images, videos, or news. This SERP feature is usually displayed for queries about topics or locations.
When searching for “London”, Google displays a vertical search with “Things to do in London”:
Related questions
Related questions boxes contain similar questions that help users explore a topic. They are very common and are often displayed when the search is a direct question.
The image below shows a “related questions” box with the search “New York:”
This SERP feature displays the three most recent tweets from a Twitter account. Tweets displayed may include images and links. Users can also scroll right to see more tweets from that account.
The image below shows this SERP feature in response to the query “CNN en español:”
 Outstanding news
Outstanding news
This SERP feature displays breaking news or trending stories related to a search. Google includes three news highlights in this feature, each containing a headline, an image, a link, and the time the story was published. This feature used to be called “In the News.”
When searching for “New York”, Google shows the main news related to this city:
 Sometimes Google also displays relevant news horizontally without images.
Sometimes Google also displays relevant news horizontally without images.
Featured Snippets
Google Featured Snippets are perhaps the best way for businesses to gain exposure in the SERPs organically, and as a result, they are often referred to as “position zero”.
According to Ahrefs, 99.58% of featured snippets are pulled from pages that are already in the top ten positions in the SERPs. Therefore, to stand a chance of reaching position zero, businesses must already rank high in the SERPs.
Here are the five main types of featured snippets:
Featured Snippet Paragraphs
To create featured snippet paragraphs, Google pulls the text and sometimes an image from a page in response to a search directly within the SERPs.
This is the most popular type of featured snippet, and is often displayed for questions that start with “how”, “what is” or “why is it”. The following image shows a featured snippet paragraph derived from the query “why is the sky blue?”:
Featured snippets in numbered list
This SERP feature usually ranks items by number or lists instructions that explain how to do something.
Here is an example of a numbered list featured snippet as a search result for “Beginners Guide to Photoshop”:
 Featured snippets in bulleted list
Featured snippets in bulleted list
This search function is almost identical to the numbered list featured snippets, except that the list is simply bulleted. These featured snippets are often displayed for unranked listings and the information displayed is often pulled from listed items.
The image below shows a bulleted list featured snippet derived from a search on flu remedies:
 Featured snippets in table
Featured snippets in table
This SERP feature displays images over a table that contains information such as statistics and rankings.
These tables often change size and layout depending on the search. And Google even pulls information from more than one source to create its own featured snippet in the SERP table.
The image below shows a tabled featured snippet showing the TV schedule :
 YouTube Featured Snippets
YouTube Featured Snippets
This SERP feature is pulled from YouTube and often shows a specific clip from a video. YouTube featured snippets are often displayed in response to “how-to” queries, or for any search that is best answered in video form.
The image below shows a YouTube featured snippet derived from the search “how to paint a car:”
 academic articles
academic articles
Scientific or research-based articles also have their own section in the Google SERPs. This is what comes up when you search for “health technology”:
 Google pulls these sources from its Google Scholar search function. Here we will find science magazines, research and similar publications.
Google pulls these sources from its Google Scholar search function. Here we will find science magazines, research and similar publications.
Related searches
Scroll to the bottom of the SERP and you’ll see related search suggestions, allowing you to do an advanced Google search. These are Google’s recommendations based on the user’s original query: maybe you’ve scrolled all the way down and haven’t found exactly what you’re looking for, so Google offers a different approach.
Related searches are presented in multiple ways. As hyperlinked text all the way to the bottom:

And you can also scroll. These are usually on top of related text-based searches or scattered throughout the SERP.
Pro Tip: Use it for your keyword and content strategy.
Paid Google SERP Features in 2021
Now that we have seen all the organic SERP features, let us take a look at the two types of paid Google SERP features in 2021.
Google Ads (formerly AdWords)
These ads are created with Google Ads , and can be used by businesses to target specific keywords . They look almost identical to regular listings, but include a small “Ad” badge before the URL as shown in the image below:
 The four most coveted ad positions are above the organic results at the top of the SERPs.
The four most coveted ad positions are above the organic results at the top of the SERPs.

However, Google also shows paid listings below the organic results at the bottom of the page. Understandably these have lower click-through rates and are therefore less expensive.
 Google Shopping
Google Shopping
The second SERP paid feature is Google Shopping. These results are shown for queries that are highly product-related, and users typically have a high purchase intent.
Paid shopping results are made up of multiple product listings. Each listing will typically contain the product title, image, seller name, and customer ratings.
They often appear at the top of the SERPs above the organic results:
 Google sometimes shows you result in the right sidebar next to the organic results. We show you what appears when searching for “fishing rod”:
Google sometimes shows you result in the right sidebar next to the organic results. We show you what appears when searching for “fishing rod”:

Google has also introduced popular product carousels in SERPs, which offer a quick list of star-rated thumbnails for searched products. This is the result when searching for “boy tennis”:
 Summary: Understanding Google SERPs
Summary: Understanding Google SERPs
We have come to the end of our guide to Google SERPs in 2021. If you have read our article, you now know what SERPs, SEO, and SEM are, as well as the various Google SERP features available and how to rank on Google.
Recall that there are two approaches to SERP marketing:
- Organic search engine optimization (SEO)
- Paid Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
The best SERP marketing strategies use both to maximize traffic.
You can learn more about SEO in our Google Featured Snippets guide and about SEM in our Google Shopping Ads guide.
Do you already know how to improve the positioning of your website? Tell us in the comments below!










